Learning Examples | Foundations | Hacking | Links
Examples > Wire Library
Master Writer/Slave Receiver
Sometimes, the folks in charge just don't know when to shut up! In some situations, it can be helpful to set up two (or more!) Arduino boards to share information with each other. In this example, two Arduinos are programmed to communicate with one another in a Master Writer/Slave Receiver configuration via the I2C synchronous serial protocol. Several functions of Arduino's Wire Library are used to accomplish this. Arduino 1, the Master, is programmed to send 6 bytes of data every half second to a uniquely addressed Slave Arduino. Once that message is received, it can then be viewed in the Slave Arduino's serial window.
The I2C protocol involves using two wires to send and receive data: a serial clock pin (SCL) that the Arduino pulses at a regular interval, and a serial data pin (SDA) over which data is sent between the two devices. As the clock pulse changes from low to high (known as the rising edge of the clock), a bit of information is transferred from the Arduino to the I2C devices over the SDA line. When the clock pin changes from high to low (the falling edge of the clock), the called upon device transmits a bit of data back to the Arduino over the same line. The initial eight bits (i.e. eight clock pulses) from the Master to Slaves contain the address of the device the Master wants data from. The bits after that contain the memory address on the Slave that the Master wants to read data from or write data to, and the data to be written, if any.
Each Slave device to have its own unique address and both master and slave devices to take turns communicating over a the same data line line. In this way, it's possible for your Arduino to communicate with many device or other Arduinos using just two pins of your microcontroller, using each device's unique address.
Hardware Required
- (2) Arduino Boards
- hook-up wire
Circuit
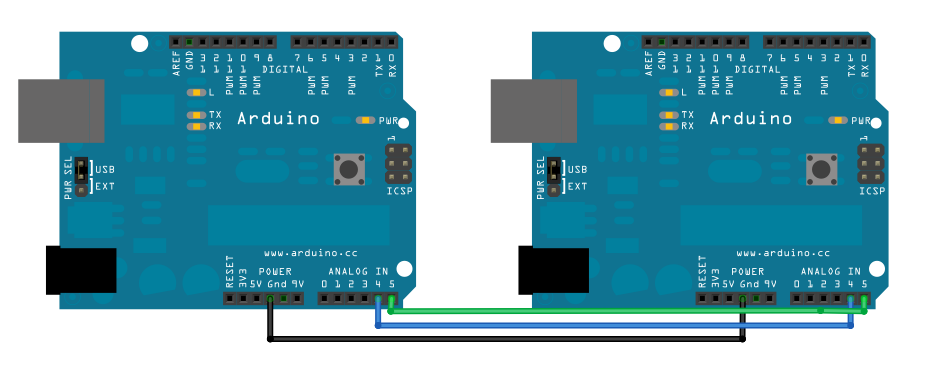
Connect pin 4 (the clock, or SCL, pin) and pin 5 (the data, or SDA, pin) on the master Arduino to their counterparts on the slave board. Make sure that both boards share a common ground. In order to enable serial communication, the slave Arduino must be connected to your computer via USB.
If powering the Arduinos independently is an issue, connect the 5V output of the Master Arduino to the VIN pin on the slave.
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic
Code
Master Writer Code - Program for Arduino 1
// by Nicholas Zambetti <http://www.zambetti.com>
// Demonstrates use of the Wire library
// Writes data to an I2C/TWI slave device
// Refer to the "Wire Slave Receiver" example for use with this
// Created 29 March 2006
// This example code is in the public domain.
#include <Wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); // join i2c bus (address optional for master)
}
byte x = 0;
void loop()
{
Wire.beginTransmission(4); // transmit to device #4
Wire.write("x is "); // sends five bytes
Wire.write(x); // sends one byte
Wire.endTransmission(); // stop transmitting
x++;
delay(500);
}
Slave Receiver Code - Program for Arduino 2
// by Nicholas Zambetti <http://www.zambetti.com>
// Demonstrates use of the Wire library
// Receives data as an I2C/TWI slave device
// Refer to the "Wire Master Writer" example for use with this
// Created 29 March 2006
// This example code is in the public domain.
#include <Wire.h>
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(4); // join i2c bus with address #4
Wire.onReceive(receiveEvent); // register event
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
}
void loop()
{
delay(100);
}
// function that executes whenever data is received from master
// this function is registered as an event, see setup()
void receiveEvent(int howMany)
{
while(1 < Wire.available()) // loop through all but the last
{
char c = Wire.read(); // receive byte as a character
Serial.print(c); // print the character
}
int x = Wire.read(); // receive byte as an integer
Serial.println(x); // print the integer
}