Learning Examples | Foundations | Hacking | Links
Examples > Sensors
Knock
This tutorial shows you how to use a Piezo element to detect vibration, in this case, a knock on a door, table, or other solid surface.
A piezo is an electronic device that generates a voltage when it's physically deformed by a vibration, sound wave, or mechanical strain. Similarly, when you put a voltage across a piezo, it vibrates and creates a tone. Piezos can be used both to play tones and to detect tones.
The sketch reads the piezos output using the analogRead() command, encoding the voltage range from 0 to 5 volts to a numerical range from 0 to 1023 in a process referred to as analog-to-digital conversion, or ADC.
If the sensors output is stronger than a certain threshold, your Arduino will send the string "Knock!" to the computer over the serial port.
Open the serial monitor to see this text.
Hardware Required
- Arduino Board
- (1) Piezo electric disc
- (1) Megohm resistor
- solid surface
Circuit
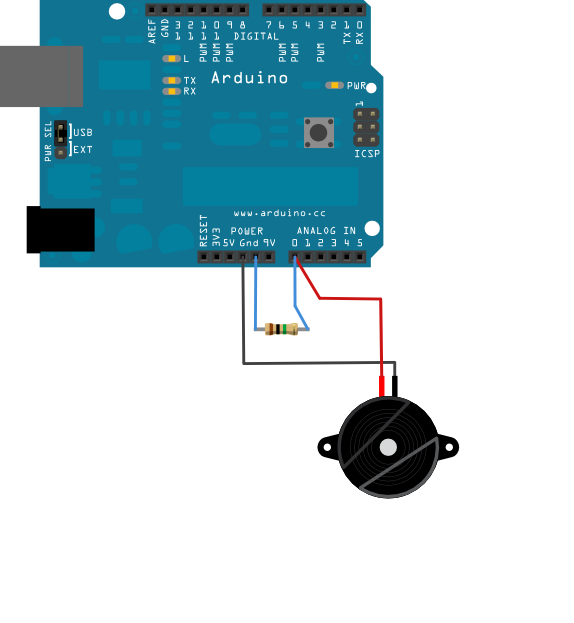
Piezos are polarized, meaning that voltage passes through them (or out of them) in a specific direction. Connect the black wire (the lower voltage) to ground and the red wire (the higher voltage) to analog pin 0. Additionally, connect a 1-megohm resistor in parallel to the Piezo element to limit the voltage and current produced by the piezo and to protect the analog input.
It is possible to acquire piezo elements without a plastic housing. These will look like a metallic disc, and are easier to use as input sensors. PIezo sensors work best when firmly pressed against, taped, or glued their sensing surface.
click the image to enlarge
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
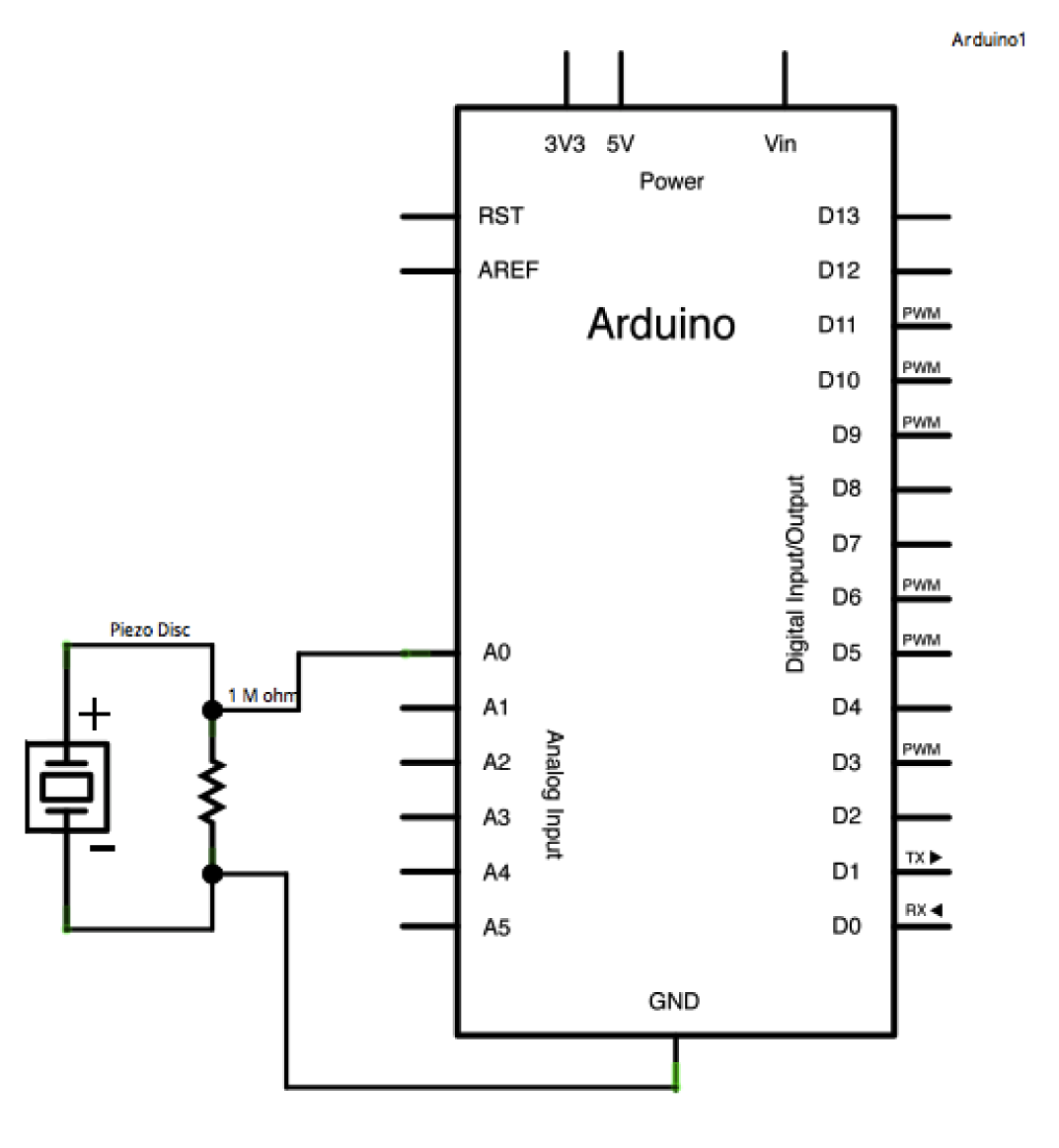
Schematic:
click the image to enlarge
A Piezo to attached to analog pin 0 with a 1-Megohm resistor
Code
In the code below, the incoming piezo data is compared to a threshold value set by the user. Try raising or lowering this value to increase your sensor's overall sensitivity.
This sketch reads a piezo element to detect a knocking sound.
It reads an analog pin and compares the result to a set threshold.
If the result is greater than the threshold, it writes
"knock" to the serial port, and toggles the LED on pin 13.
The circuit:
* + connection of the piezo attached to analog in 0
* - connection of the piezo attached to ground
* 1-megohm resistor attached from analog in 0 to ground
http://arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Knock
created 25 Mar 2007
by David Cuartielles <http://www.0j0.org>
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
*/
// these constants won't change:
const int ledPin = 13; // led connected to digital pin 13
const int knockSensor = A0; // the piezo is connected to analog pin 0
const int threshold = 100; // threshold value to decide when the detected sound is a knock or not
// these variables will change:
int sensorReading = 0; // variable to store the value read from the sensor pin
int ledState = LOW; // variable used to store the last LED status, to toggle the light
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // declare the ledPin as as OUTPUT
Serial.begin(9600); // use the serial port
}
void loop() {
// read the sensor and store it in the variable sensorReading:
sensorReading = analogRead(knockSensor);
// if the sensor reading is greater than the threshold:
if (sensorReading >= threshold) {
// toggle the status of the ledPin:
ledState = !ledState;
// update the LED pin itself:
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
// send the string "Knock!" back to the computer, followed by newline
Serial.println("Knock!");
}
delay(100); // delay to avoid overloading the serial port buffer
}
See Also:
pinMode()analogRead()if()serial.begin()serial.print()- AnalogInput - Use a potentiometer to control the blinking of an LED.
- AnalogInOutSerial - read an analog input, map its values, and then use that information to dim or brighten an LED.
- Memsic2125 - read a two axis accelerometer.
- ADXL3xx - read a ADXL3xx accelerometer.
- Ping - detect objects with an ultrasonic range finder.