Learning Examples | Foundations | Hacking | Links
Examples > Libraries > LiquidCrystal
LiquidCrystal - "Hello World!"
The LiquidCrystal library allows you to control LCD displays that are compatible with the Hitachi HD44780 driver. There are many of them out there, and you can usually tell them by the 16-pin interface.
This example sketch prints "Hello World!" to the LCD and shows the time in seconds since the Arduino was reset.

output of the sketch on a 2x16 LCD
The LCDs have a parallel interface, meaning that the microcontroller has to manipulate several interface pins at once to control the display. The interface consists of the following pins:
A register select (RS) pin that controls where in the LCD's memory you're writing data to. You can select either the data register, which holds what goes on the screen, or an instruction register, which is where the LCD's controller looks for instructions on what to do next.
A Read/Write (R/W) pin that selects reading mode or writing mode
An Enable pin that enables writing to the registers
8 data pins (D0 -D7). The states of these pins (high or low) are the bits that you're writing to a register when you write, or the values you're reading when you read.
There's also a display constrast pin (Vo), power supply pins (+5V and Gnd) and LED Backlight (Bklt+ and BKlt-) pins that you can use to power the LCD, control the display contrast, and turn on and off the LED backlight, respectively.
The process of controlling the display involves putting the data that form the image of what you want to display into the data registers, then putting instructions in the instruction register. The LiquidCrystal Library simplifies this for you so you don't need to know the low-level instructions.
The Hitachi-compatible LCDs can be controlled in two modes: 4-bit or 8-bit. The 4-bit mode requires seven I/O pins from the Arduino, while the 8-bit mode requires 11 pins. For displaying text on the screen, you can do most everything in 4-bit mode, so example shows how to control a 2x16 LCD in 4-bit mode.
Hardware Required
- Arduino Board
- LCD Screen (compatible with Hitachi HD44780 driver)
- 10k Potentiometer
- breadboard
- hook-up wire
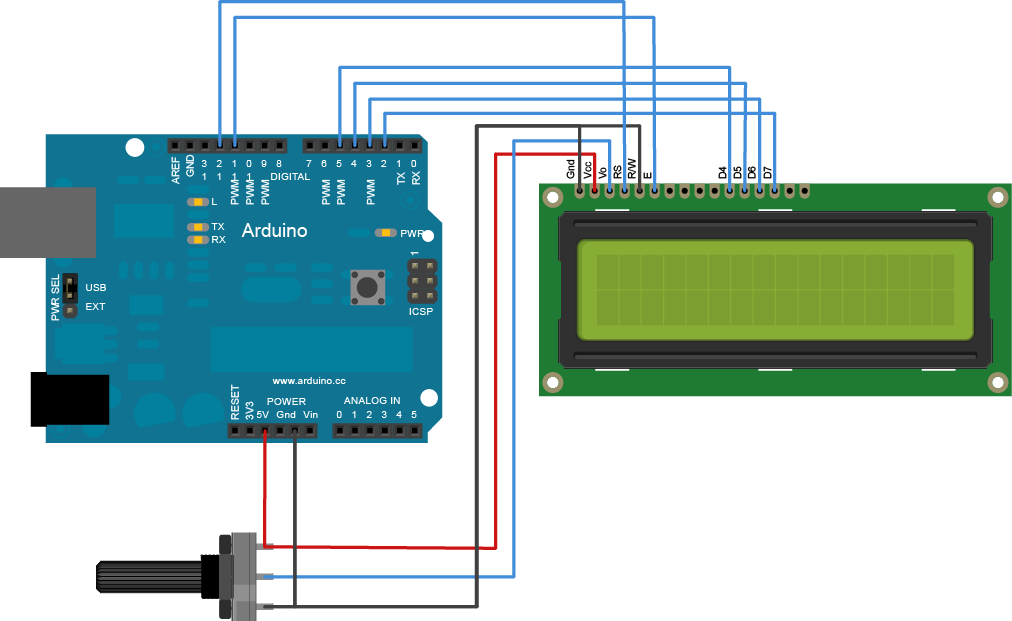
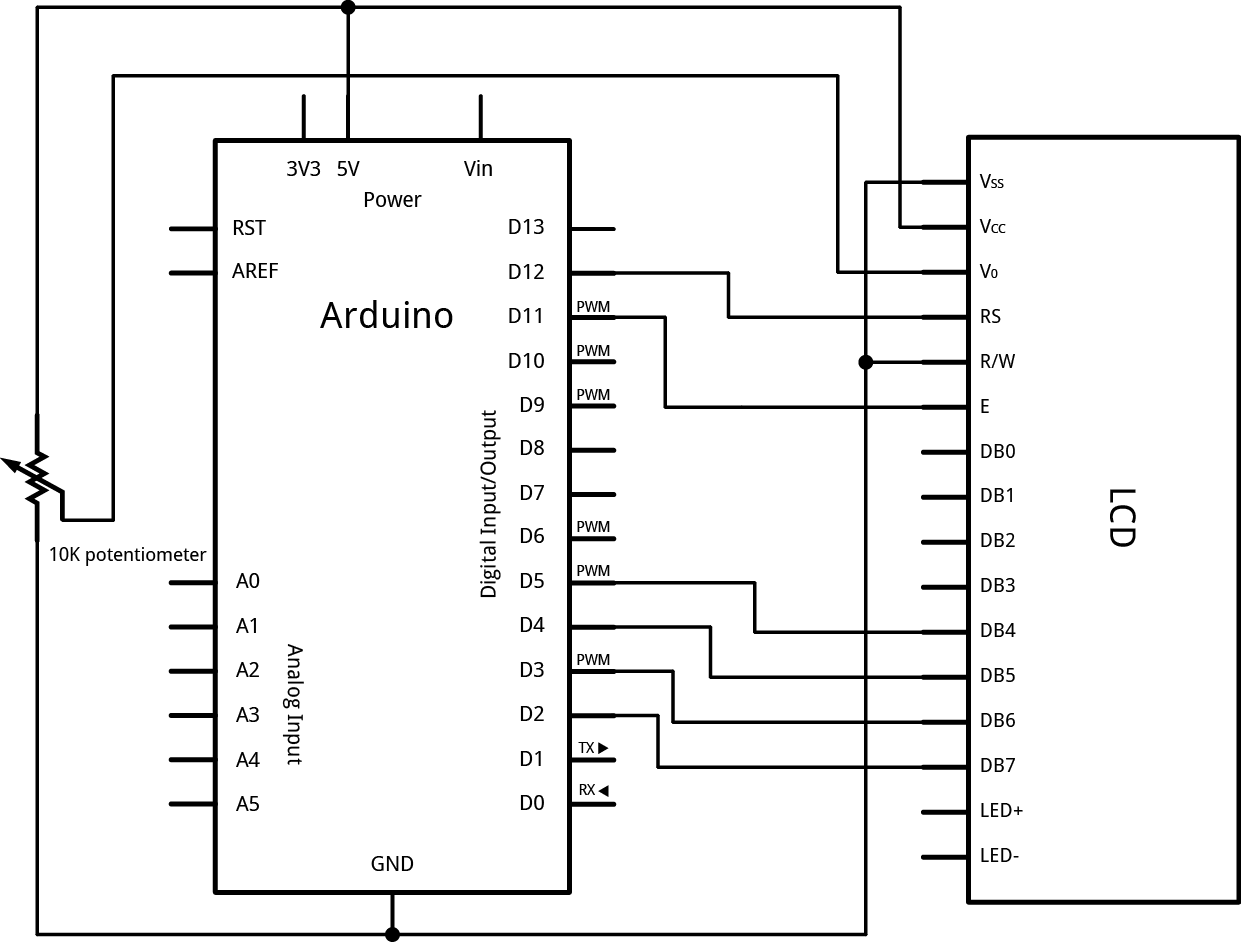
Circuit
To wire your LED screen to your Arduino, connect the following pins:
- LCD RS pin to digital pin 12
- LCD Enable pin to digital pin 11
- LCD D4 pin to digital pin 5
- LCD D5 pin to digital pin 4
- LCD D6 pin to digital pin 3
- LCD D7 pin to digital pin 2
Additionally, wire a 10K pot to +5V and GND, with it's wiper (output) to LCD screens VO pin (pin3).
click the images to enlarge
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Code
LiquidCrystal Library - Hello World
Demonstrates the use a 16x2 LCD display. The LiquidCrystal
library works with all LCD displays that are compatible with the
Hitachi HD44780 driver. There are many of them out there, and you
can usually tell them by the 16-pin interface.
This sketch prints "Hello World!" to the LCD
and shows the time.
The circuit:
* LCD RS pin to digital pin 12
* LCD Enable pin to digital pin 11
* LCD D4 pin to digital pin 5
* LCD D5 pin to digital pin 4
* LCD D6 pin to digital pin 3
* LCD D7 pin to digital pin 2
* LCD R/W pin to ground
* 10K resistor:
* ends to +5V and ground
* wiper to LCD VO pin (pin 3)
Library originally added 18 Apr 2008
by David A. Mellis
library modified 5 Jul 2009
by Limor Fried (http://www.ladyada.net)
example added 9 Jul 2009
by Tom Igoe
modified 22 Nov 2010
by Tom Igoe
This example code is in the public domain.
http://arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/LiquidCrystal
*/
// include the library code:
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
// initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(12, 11, 5, 4, 3, 2);
void setup() {
// set up the LCD's number of columns and rows:
lcd.begin(16, 2);
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.print("hello, world!");
}
void loop() {
// set the cursor to column 0, line 1
// (note: line 1 is the second row, since counting begins with 0):
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
// print the number of seconds since reset:
lcd.print(millis()/1000);
}
See Also:
lcd.begin()lcd.print()lcd.setCursor()- Liquid Crystal Library
- Blink: control of the block-style cursor.
- Cursor: control of the underscore-style cursor.
- Display: quickly blank the display without losing what's on it.
- TextDirection: control which way text flows from the cursor.
- Scroll: scroll text left and right.
- Serial input: accepts serial input, displays it.
- SetCursor: set the cursor position.
- Autoscroll: shift text right and left.